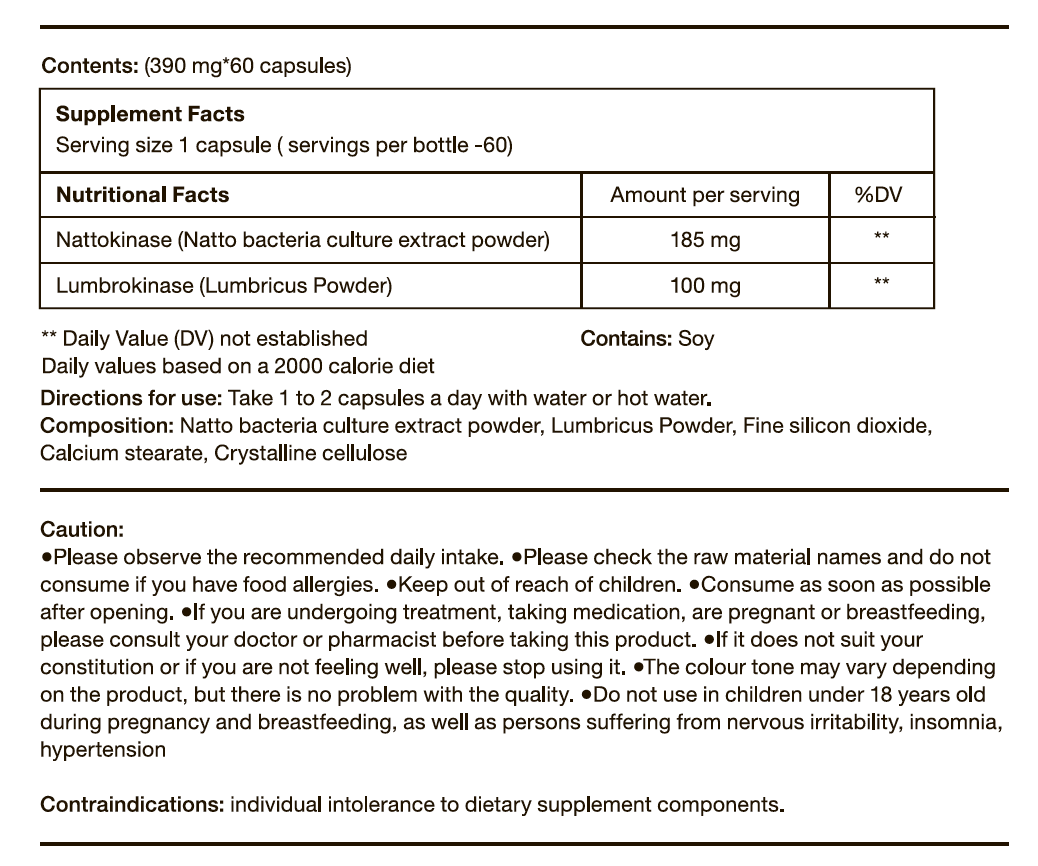
Nattokinase with Lumbrokinase
2024/12/11
Nattokinase with Lumbrokinase
Cardiovascular support
Nattokinase and lumbrokinase are enzymes known for their fibrinolytic activity, meaning they can help break down fibrin, a protein involved in blood clotting.
Nattokinase is derived from natto, a traditional Japanese fermented soybean dish.
Lumbrokinase is a group of highly stable fibrinolytic enzymes originally extracted from the earthworm *Lumbricus rubellus*.
Features:
- Potent Fibrinolysis: Like nattokinase, lumbrokinase acts as a potent fibrinolytic agent. However, it has been found to be more stable and effective in various conditions, partly due to its complex enzymatic composition .
- Plasminogen Activation: Lumbrokinase not only acts directly on fibrin but also enhances the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin, contributing to its effective clot-dissolving capabilities .
- Anti-Adhesive and Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Lumbrokinase has been shown to reduce cellular adhesion and inflammatory responses, which are beneficial in preventing post-surgical adhesions and other complications .
-Potential in Cancer Therapy: Lumbrokinase has been researched for its application in cancer therapy, particularly in its ability to inhibit tumor metastasis and growth. It is considered for use alongside traditional cancer treatments, providing a multifaceted approach to therapy .
-Cardiovascular Health: There is evidence suggesting that lumbrokinase can improve cardiovascular health by enhancing blood flow, reducing blood viscosity, and improving overall circulation. This makes it a valuable supplement for those at risk of heart disease .
-Wound Healing: Recent studies have explored the use of lumbrokinase in wound healing. Its enzymatic action can help in reducing inflammation and promoting faster tissue repair .
While both lumbrokinase and nattokinase share some similar enzymatic properties, particularly their fibrinolytic activity, there are notable differences:
-Complexity of Enzymes: Lumbrokinase consists of multiple enzymes, which may contribute to its broader therapeutic potential and stronger fibrinolytic activity compared to nattokinase, which primarily contains a single enzyme.
-Nattokinase is predominantly recognized for its benefits in cardiovascular health, particularly in improving blood flow and reducing clot risks. In contrast, lumbrokinase has been studied for a wider array of applications, including anti-tumor effects and potential use in cancer therapy .
Both enzymes work by dissolving fibrin, potentially improving blood flow and reducing the risk of blood clots. The combination of nattokinase and lumbrokinase offers a promising approach to managing vascular-related eye conditions through their fibrinolytic and anti-inflammatory properties. Ongoing research will help clarify their role and effectiveness in ophthalmologic treatments.
Potential Ophthalmologic Applications:
1. Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO):This condition involves the blockage of veins that carry blood away from the retina, leading to vision loss. The fibrinolytic activity of nattokinase and lumbrokinase may help manage and prevent this condition.
2. Diabetic Retinopathy: Patients with diabetes can develop this eye condition, which affects blood vessels in the retina. Improving blood flow and reducing clot formation may be beneficial in managing diabetic retinopathy.
3. Glaucoma: While primarily treated through pressure reduction, improving overall blood flow to the optic nerve may provide additional benefits in managing glaucoma.
Nattokinase and Lumbrokinase Activity Against Biofilm.
Nattokinase exhibits activity against biofilms, particularly those formed by bacteria like cariogenic streptococci. The enzyme interferes with the biofilm formation process, possibly due to its proteolytic activity which can disrupt the extracellular matrix that holds the biofilm together. For example:
- Interference with Cariogenic Streptococci: Nattokinase has shown potential in interfering with the biofilm formation of cariogenic streptococci, which are significant contributors to dental caries .
- Potential Against Enterococcal Biofilms: Some studies suggest that derivatives from the Bacillus subtilis natto, which produces nattokinase, might inhibit biofilm formation by Enterococcus faecalis, which is known for its role in various infections, including endocarditis .
Lumbrokinase also displays potential against biofilms, though the specific studies are fewer compared to nattokinase. The enzyme complex appears to help in disrupting biofilms, which could enhance the effectiveness of treatments against chronic infections where biofilms are a factor. For instance:
- Effectivity in Disrupting Biofilms: Lumbrokinase has been noted to be effective in breaking up biofilms, particularly in medical conditions where these structures contribute to chronic infection and resistance to treatment .
Safety and Considerations:
- Bleeding Risk: As both enzymes have potent anticoagulant properties, there is an increased risk of bleeding, particularly in patients taking blood thinners or with bleeding disorders.
- Allergic Reactions:Caution is advised for those with soy allergies when using nattokinase.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Due to a lack of safety data, use in pregnant or breastfeeding women is not recommended.References:
1. Fujita, M., Hong, K., Ito, Y., Misawa, S., Takeuchi, N., Kariya, K., & Nishimuro, S. (1995). Transport of nattokinase across the rat intestinal tract. *Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 18*(9), 1194-1196.
2. Kim, J.Y., Gum, S.N., Paik, J.K., Lim, H.H., Kim, K.C., Ogasawara, K., Inoue, K., Park, S., Jang, Y., & Lee, J.H. (2008). Effects of nattokinase on blood pressure: a randomized, controlled trial. *Hypertension Research, 31*(8), 1583-1588.
3. Mihara, H., Sumi, H., Yoneta, T., Mizumoto, H., Ikeda, R., Seiki, M., & Maruyama, M. (1991). A novel fibrinolytic enzyme extracted from the earthworm, *Lumbricus rubellus*. *Japanese Journal of Physiology, 41*(3), 461-472.
4. Jin, L., et al. (2000) found that lumbrokinase improves circulation and has a protective effect on retinal ganglion cells in rat models of retinal ischemia.
5. Zhang, Z., et al. (2008) demonstrated that lumbrokinase could effectively treat and prevent complications in patients with diabetic retinopathy.
6. Dach, J. "Fibrinolytic and Proteolytic Enzymes Medical Use" highlights the antithrombotic benefits of lumbrokinase and its implications for cardiovascular health .
7. Altaf F, Wu S, Kasim V. Role of Fibrinolytic Enzymes in Anti-Thrombosis Therapy. Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 28;8:680397
8. Cooper EL, Ma MJ. Understanding nutrition and immunity in disease management. J Tradit Complement Med. 2017 Jan 16;7(4):386-391.
9. Weng, Y.; Yao, J.; Sparks, S.; Wang, K.Y. Nattokinase: An Oral Antithrombotic Agent for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 523.
10. Narisawa N., Kawasaki Y., Nakashima K., Abe S Interference effects of proteolytic nattokinase on biofilm formation of cariogenic streptococci Food Preserv Sci 2014 6;40: 272-277